Selective separation of radionuclides from environmental matrices using proprietary solid-phase extraction systems: A review
Associate Professor Ismail Md. Mofizur Rahman
Research Overview
Precise and rapid determination of radionuclides (RNs) in the environment is essential for environmental monitoring, radiological protection, and radioactive waste management, as well as following the unprecedented release of RNs after nuclear accidents, e.g., Chornobyl, Fukushima. In this regard, sample preparation, which is an error-prone step in RN analysis, needs more attention to improve selectivity and sensitivity of analytical measurements by sample clean-up or pre-concentration.
Solid-phase extraction (SPE) is an effective sample preparation technique capable of selectively separating target RNs from other matrix ions in environmental samples. Commercially available proprietary SPE products, packaged in columns, cartridges, or disk formats, have been widely used for sample purification in RN analysis. They have high affinity and selectivity for target RNs, and their reusability and ease of large-scale production make them more economical than other options. Since there have not been any reviews regarding selective separation of RNs using proprietary SPE products, this work reviews approaches that have been adopted for isolation of RNs (Cs, Sr, Tc, Th, U, Np, Pu, Am, and Cm) from environmental matrices. The review assumably provides information on selecting particle-based SPE-assisted sample preparation techniques to separate and analyze RNs in environmental matrices.
Figure
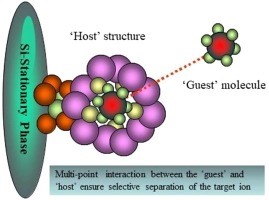
The Significance of the Study
It is the first review of processes developed to selectively separate RNs (Cs, Sr, Tc, Th, U, Np, Pu, Am, and Cm) using proprietary macro-SPEs.
Publication
The updated version of the article is available online on 19 July 2022.
| Journal | Microchemical Journal |
|---|---|
| Title | Selective separation of radionuclides from environmental matrices using proprietary solid-phase extraction systems: A review |
| URL | https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2022.107637 |
| Authors | M. Ferdous Alam,a, b, * Zinnat A. Begum,c, f, Yoshiaki Furusho,d, Hiroshi Hasegawa,e, Ismail M.M. Rahman,f, * aGraduate School of Symbiotic Systems Science and Technology, Fukushima University bInstitute of Nuclear Science and Technology, Atomic Energy Research Establishment cDepartment of Civil Engineering, Southern University Bangladesh dGL Sciences Inc. eInstitute of Science and Engineering, Kanazawa University fInstitute of Environmental Radioactivity, Fukushima University *Corresponding author(s) |
